Ovarian Cancer Tumor Ultrasound
The process of tvus uses an ultrasound wand into the vagina in order to find any mass or lump in the ovary or uterus though not all the masses found would essentially be tumor.
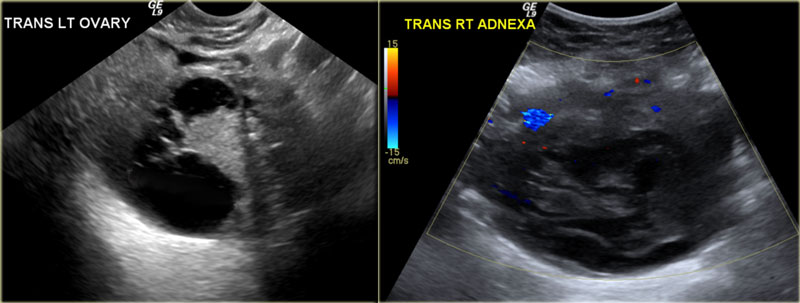
Ovarian cancer tumor ultrasound. Pathology subtypes primary ovarian tumors. Tvus transvaginal ultrasound is a test that uses sound waves to look at the uterus fallopian tubes and ovaries by putting an ultrasound wand into the vagina. When it is used for screening most of the masses found are not cancer. Ultrasound scan you might have an external ultrasound of your lower tummy pelvis or a vaginal ultrasound to help diagnose ovarian cancer.
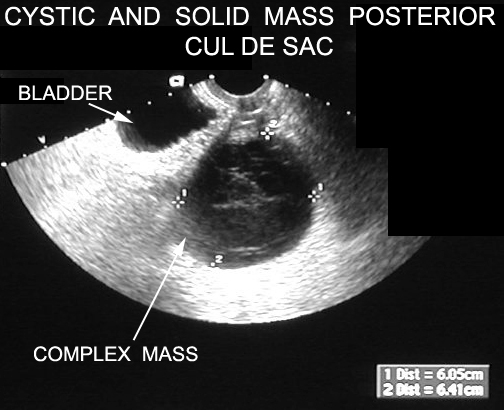
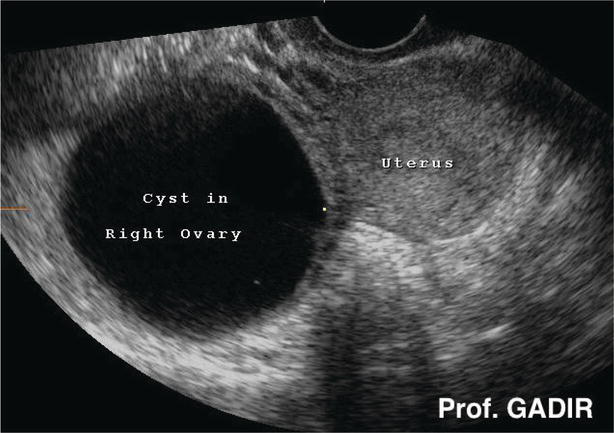
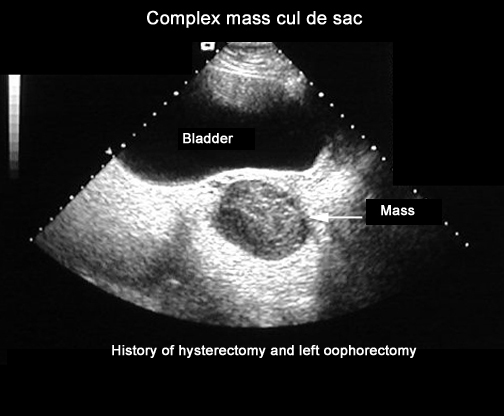
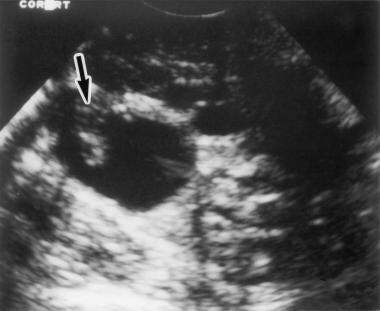
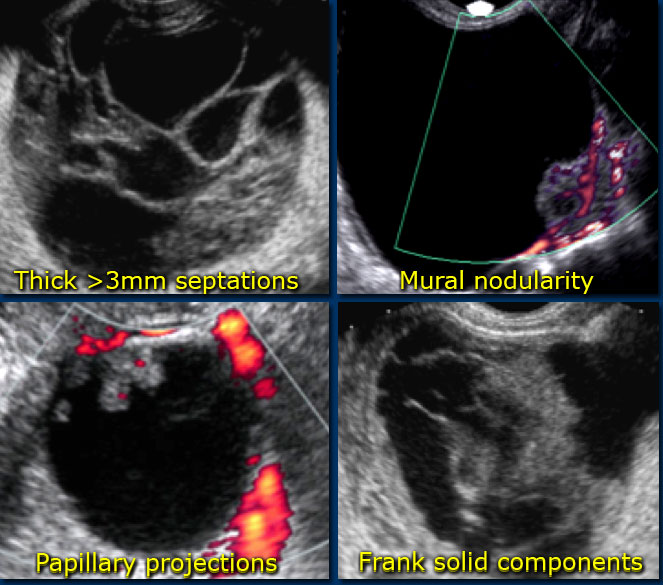
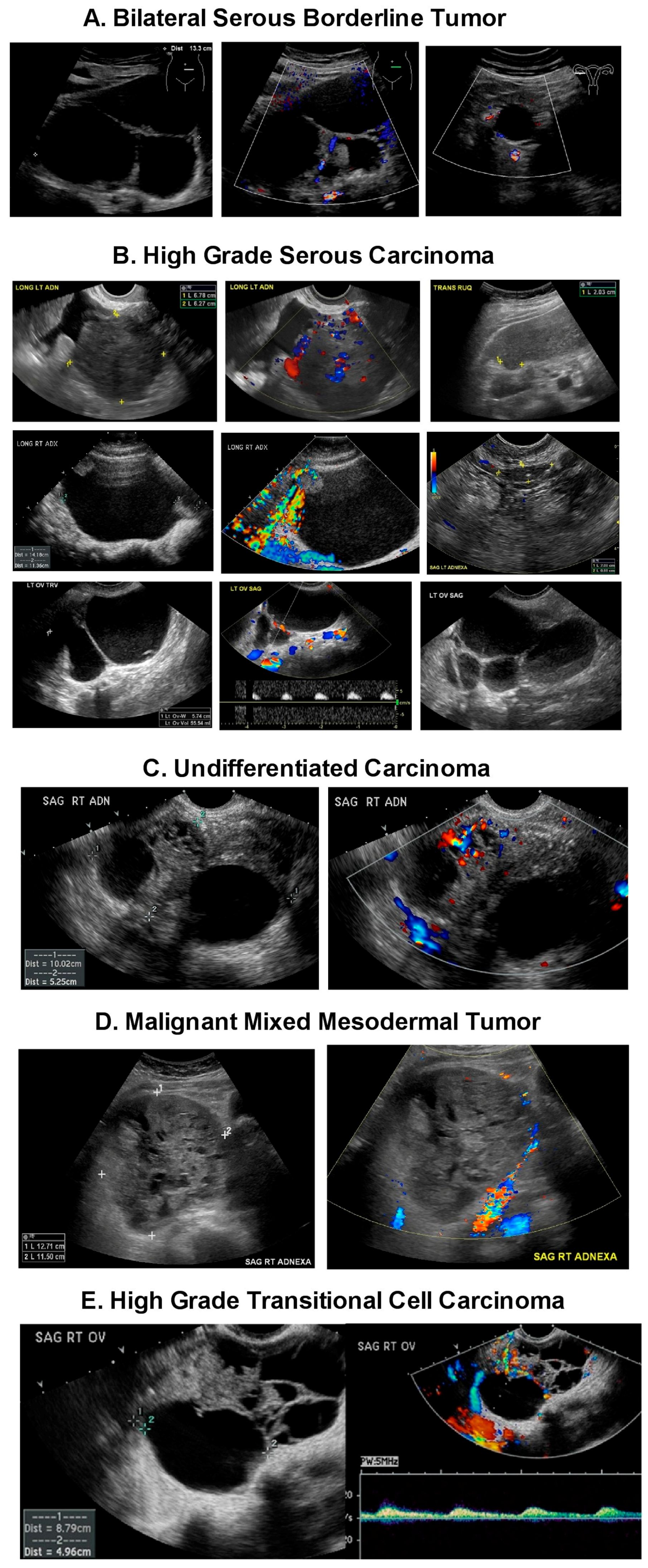
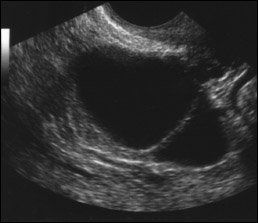
It can even see inside the ovaries. This article focuses on the general classification of ovarian tumors. By the time the changes of ovarian cancer are detectable by ultrasound most ovarian cancers are well beyond the early stage of the disease. In cases of ovarian cancer ultrasound usually reveals complex cysts on one or both ovaries multiple solid masses nodule on the bowel or excess pelvic and or abdominal fluid.
Computed tomography ct scans use x rays to create. For ovarian cancer the biopsy is most commonly done by removing the tumor during surgery. If cancer is suspected the next step. In rare cases a suspected ovarian cancer may be biopsied during a laparoscopy procedure or with a needle placed directly into the tumor through the skin of the abdomen.
Usually the needle will be guided by either ultrasound or ct scan. Ovarian tumors are relatively common and account for 6 of female malignancies. Ultrasound scans use high frequency sound waves to create a picture of a part of the body. It can show the ovaries womb and surrounding structures.
Transvaginal ultrasound or tvus usually prescribed for screening and detecting ovarian cancer uses sound waves for looking inside the uterus ovaries and fallopian tubes. A good ultrasound image can identify a mass and determine if it s a tumor solid or a cyst fluid filled. But these scans can t determine whether the abnormality is cancer. For specific features refer to the subarticles.