Lichen Sclerosis Pathology

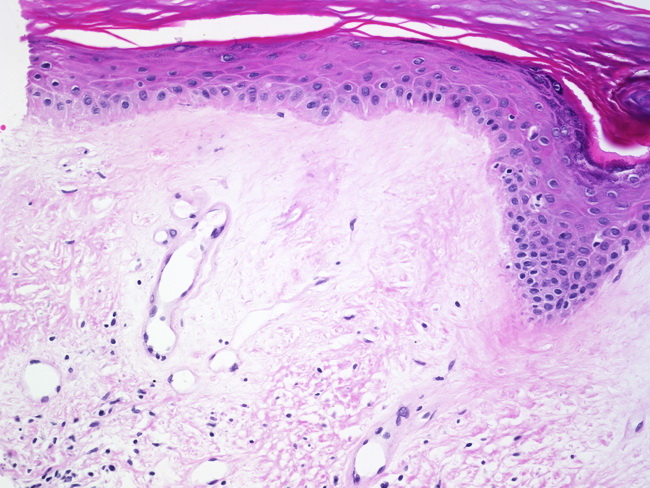
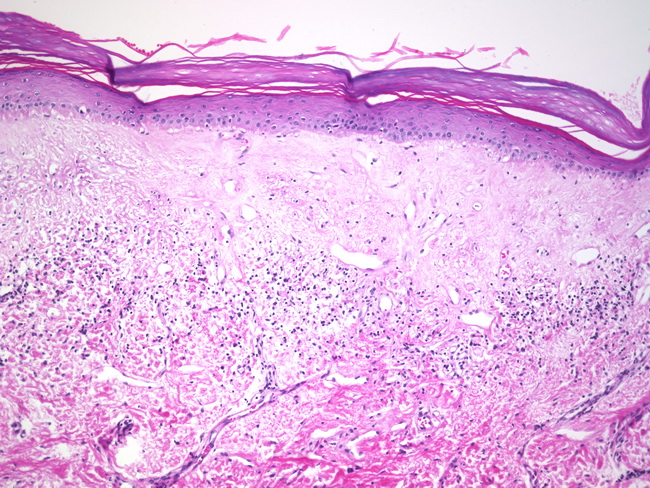
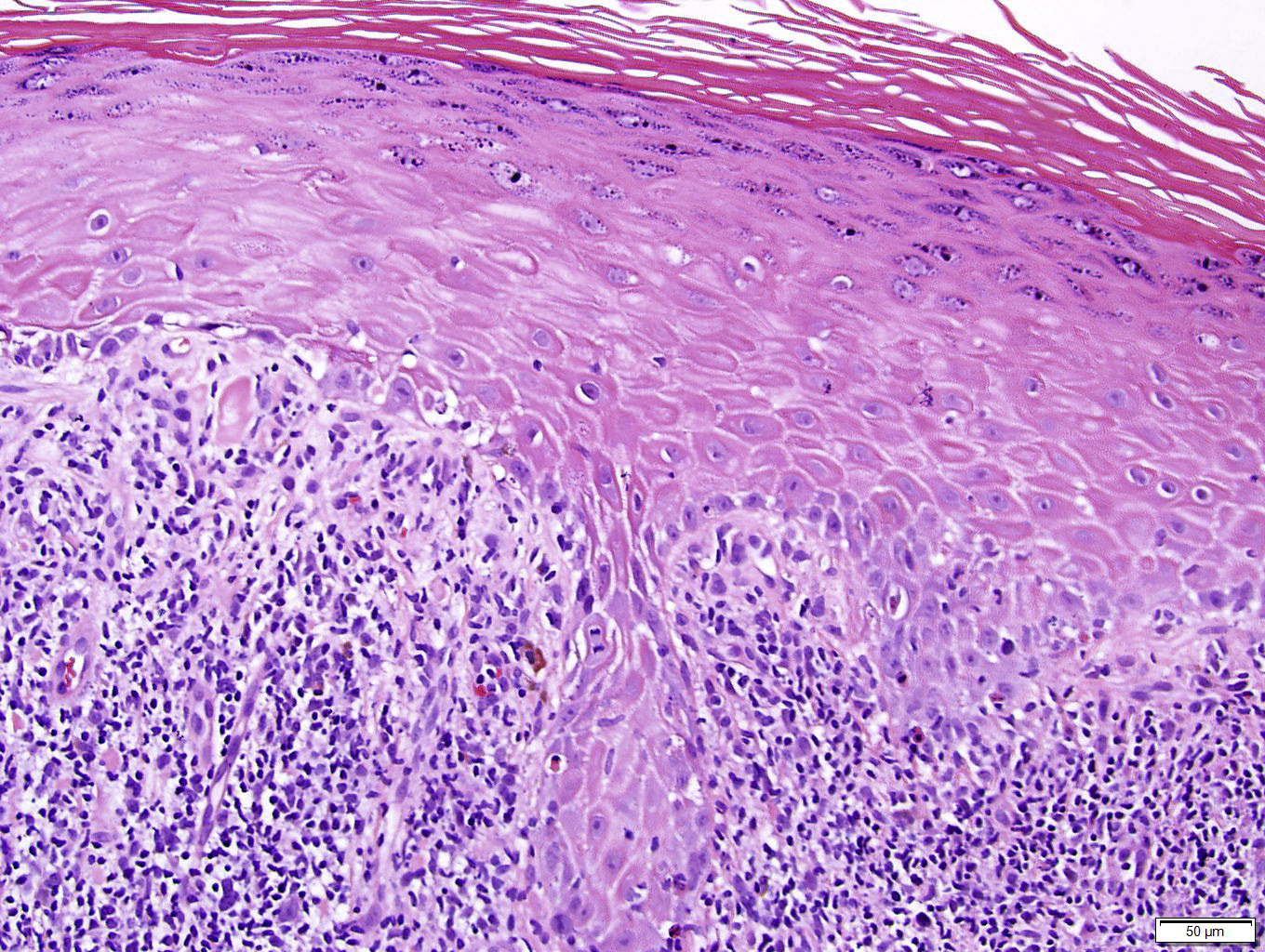
Epithelium may have prominent acanthosis with prominent granular layer and hyperkeratosis.
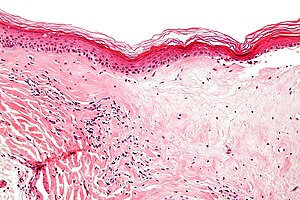
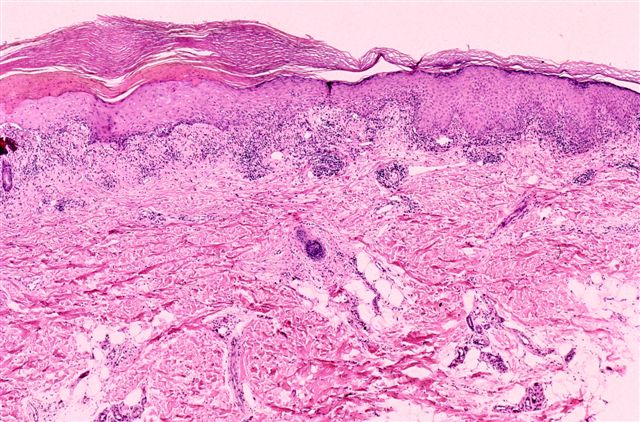
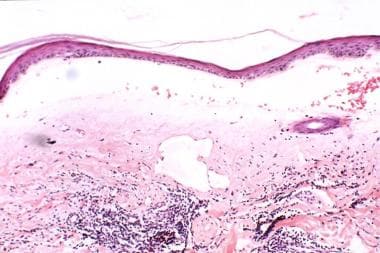
Lichen sclerosis pathology. In this condition the overlying epidermis and superficial dermis is spared. There is no acanthosis. There is no basal nuclear atypia. Overlap can occur where superficial and deep changes co exist.
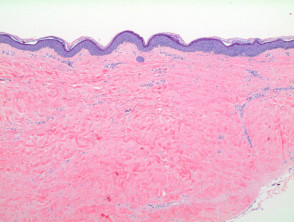
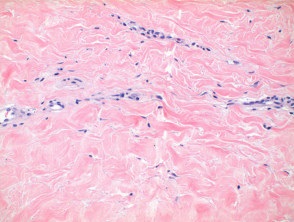
The sections show skin with loss of the rete ridges hyperkeratosis and marked fibrosis of the superficial dermis. But it can also affect your upper arms torso and breasts. Differential diagnosis of lichen sclerosus pathology scleroderma. Few scattered lymphocytes are seen in the dermis.
It creates patches of shiny white skin that s thinner than normal. Lichen sclerosus is a chronic skin disorder that is more common in women most often affecting the external part of the vagina vulva or the area around the anus. In older lesions acanthosis may be absent and epithelium may be thinned with loss of rete ridges. A granular layer is present.
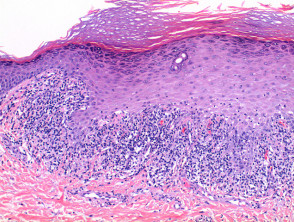
Lichen sclerosus is a rare skin condition that usually shows up on your genital or anal areas. The condition can affect any part of your body but it most commonly affects skin in the. Sclerotic phase of lichen sclerosus with active inflammation. In men it typically affects the tip of the penis.
The inflammatory infiltrate is typically sparse and around deep adnexal and vascular structures. Lichen sclerosus ls is a chronic inflammatory dermatosis of unknown cause that most commonly affects the genitalia vulvar and penile lichen sclerosus but it can occur at any skin site. Sclerotic phase of lichen sclerosus. Liquefaction necrosis and colloid bodies may be present within basal epithelial cells.
The condition mostly affects adult women. Lichen sclerosus is a skin condition. Anyone can get lichen sclerosus but postmenopausal women are at higher risk.