Cyst Ovarian Cancer Ultrasound Vs Normal
Ovarian cysts are often identified when an ultrasound examination is performed for another reason.
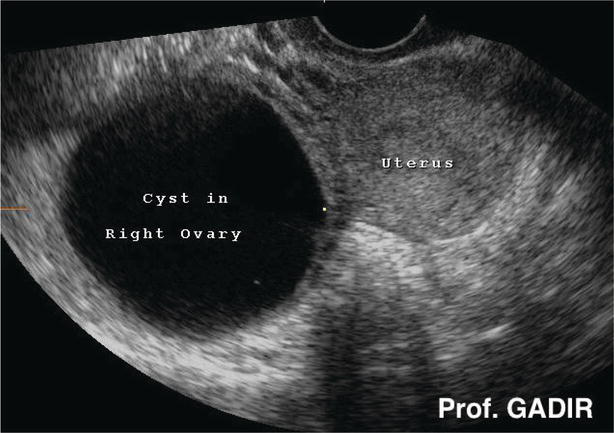
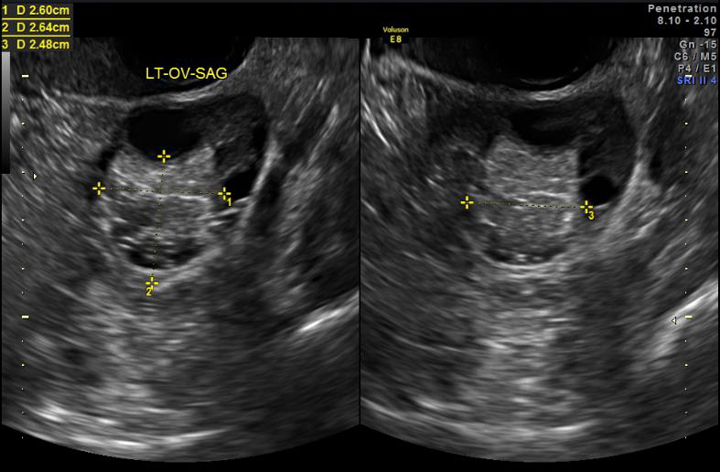
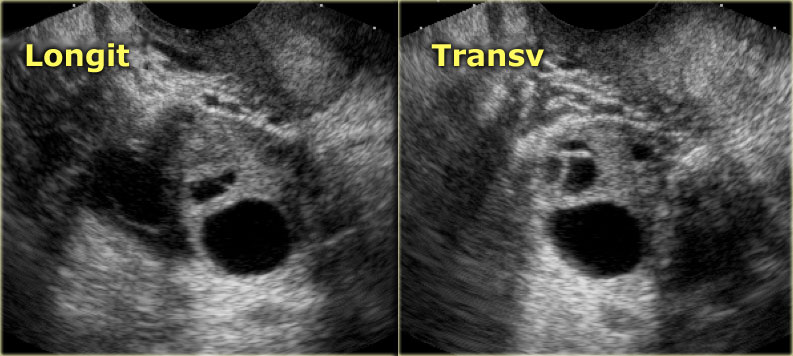
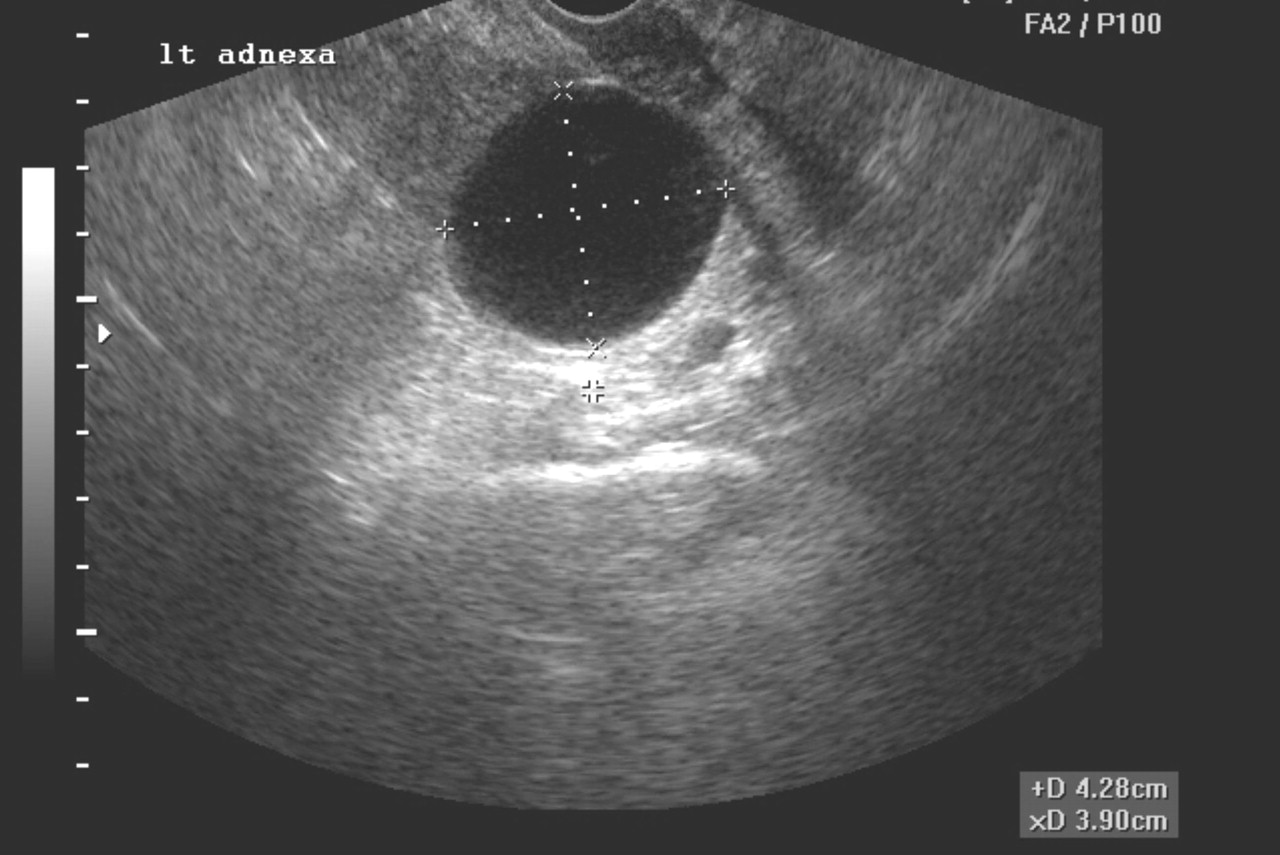
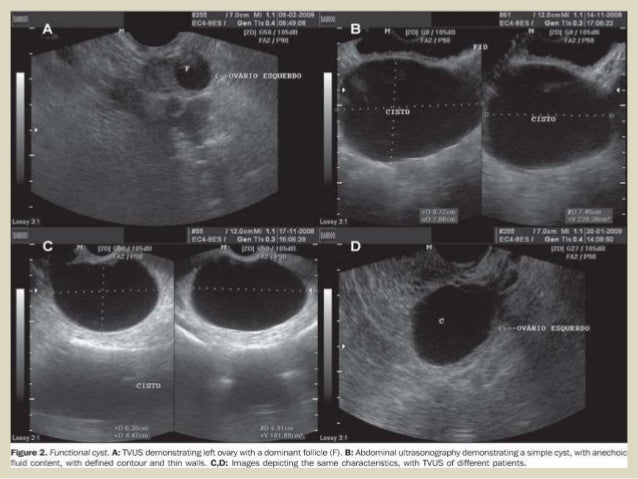
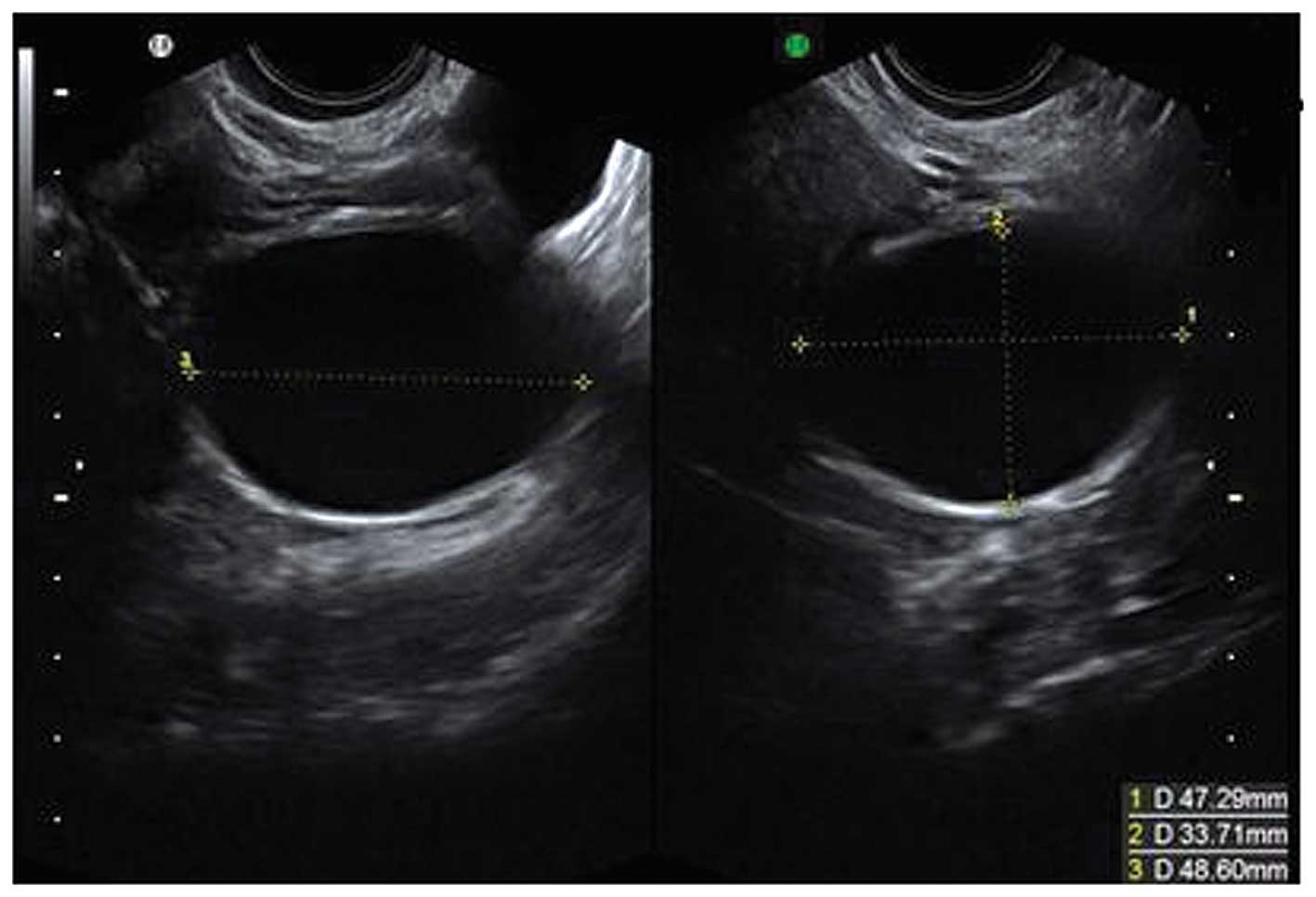
Cyst ovarian cancer ultrasound vs normal. A simple appearing and fluid filled structure without solid growths and no extra blood flow likely indicate a benign cyst. Ovarian cancer is misdiagnosed as cyst by many patients and if a patient has experienced any of the previously mentioned signs and symptoms then it is always advised to consult the doctor right away. Small cystic ovarian structures should be considered normal ovarian follicles unless the patient is pre pubertal post menopausal pregnant or the mean diameter is 3 cm see the 1 2 3 rule. Cancer is vastly different.
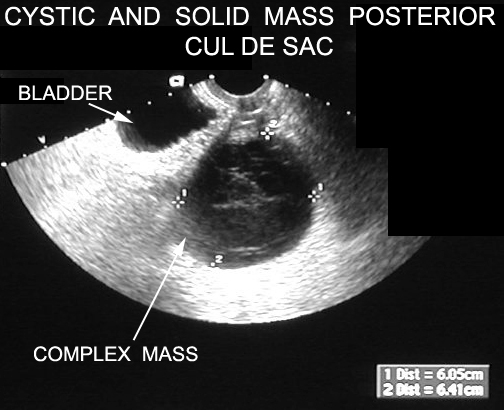
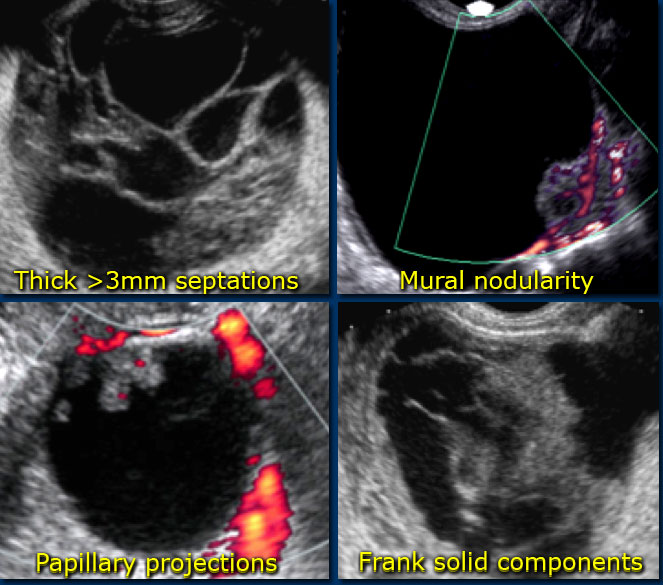
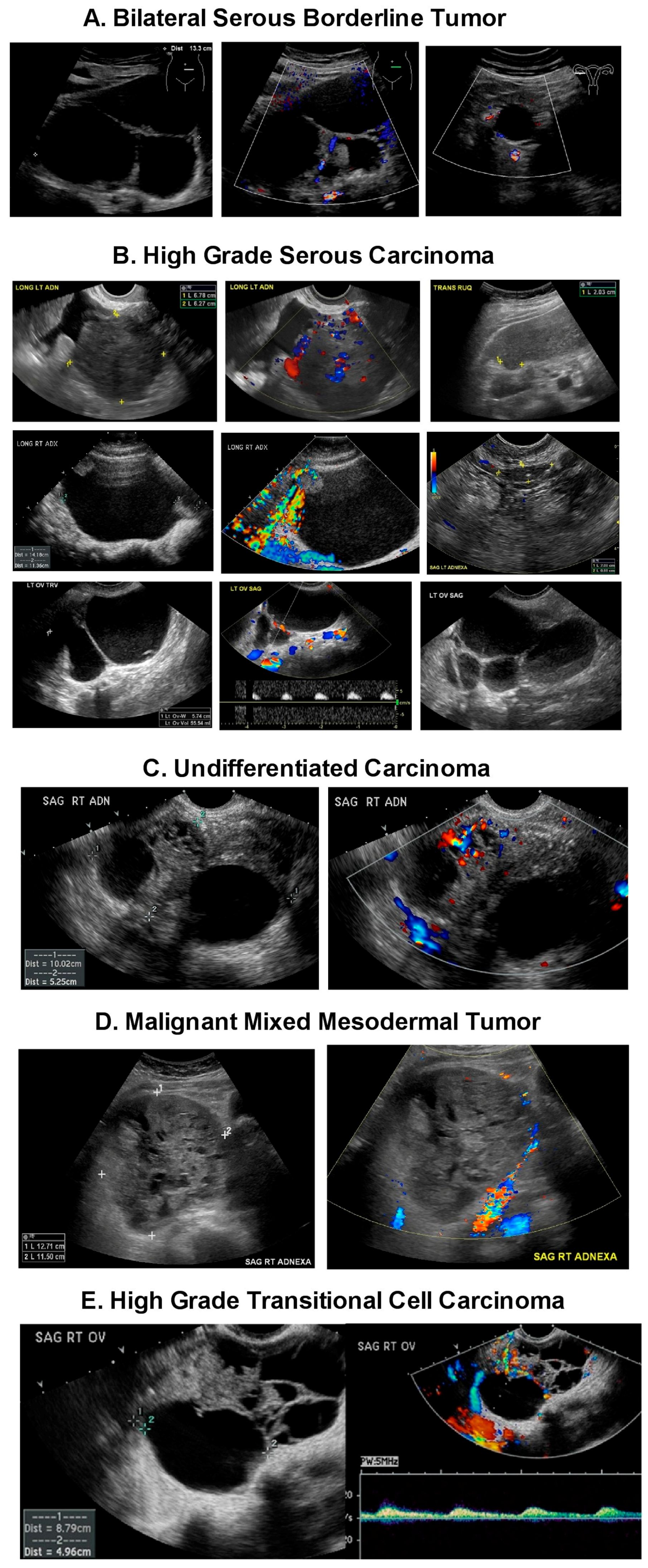
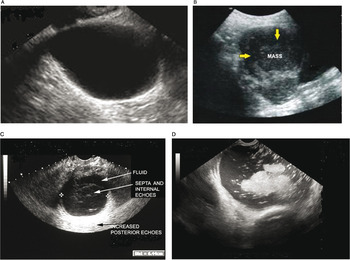
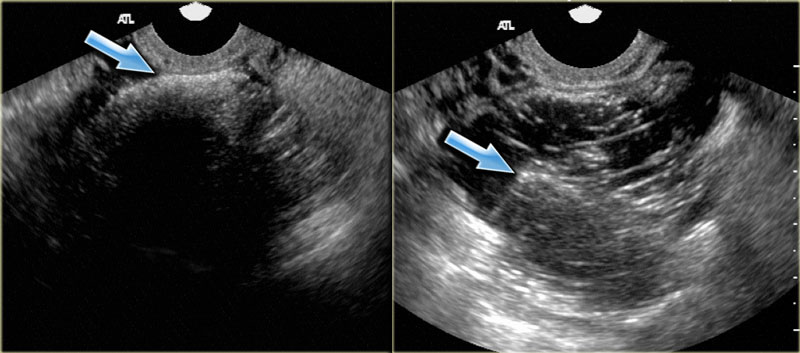
The features of a benign or malignant ovarian cyst can often be seen with an ultrasound. In cases of ovarian cancer ultrasound usually reveals complex cysts on one or both ovaries multiple solid masses nodule on the bowel or excess pelvic and or abdominal fluid. For example cysts that contain papillary structures solid areas and increased vascularity are more likely to be malignant. Ovarian cysts with all of the features of ovarian cancer warrant the recommendation of removal of the cyst to definitively determine if it is benign or malignant.
If there is any doubt whether a growth is benign or malignant the growth is removed and biopsied. Functional cysts can produce hormones. Mean diameter 3 cm ovarian follicle. It is impossible to tell the difference between ovarian cysts and ovarian cancer from the symptoms alone but ovarian cysts are much more common.
Transvaginal ultrasound especially 3d ultrasound can help physicians differentiate between benign simple cysts and potentially cancerous complex ovarian masses. By the time the changes of ovarian cancer are detectable by ultrasound most ovarian cancers are well beyond the early stage of the disease. Ovarian cancer can be a frightening diagnosis with five year relative survival rates that range from 93 to 19 for epithelial ovarian cancer depending on the stage when the cancer was found. The usual diagnostic methods in cases where there is a suspicion of ovarian cysts or ovarian cancer include the use of mri and ultrasound.
The treatment for ovarian cysts vs. Ovarian cysts usually resolve without treatment and most disappear within one to two months. Mri of ovarian cysts ovarian cancer is the second most common of all gynecologic malignancies and it is the leading cause of death in this category of disease. An ultrasound may distinguish cysts from cancerous tumors but it is inexact.