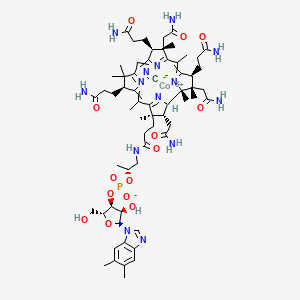
Vitamin B 12 Structure

Methionine is required for the formation of s adenosylmethionine a.
Vitamin b 12 structure. The vitamin which is unique in that it contains a metallic ion cobalt has a complex chemical structure as shown. The common forms of vitamin b include vitamin b1 b2 b3 b6 and b12 cyanocobalamin except for niacin when given in high doses there is no evidence that the other b vitamins. Vitamin b 12 is a large molecule that contains an atom of cobalt. Vitamin b 12 is.
Vitamin b 12 is derived from a tetrapyrrolic structural framework created by the enzymes deaminase and cosynthetase which transform aminolevulinic acid via porphobilinogen and hydroxymethylbilane to uroporphyrinogen iii. Vitamin b 12 aids in the development of red blood cells in higher animals. Vitamin b refers to several water soluble vitamins often found together in foods all of which are necessary for normal growth and metabolism but none of which are synthesized in adequate amounts by humans. Dangerous properties of industrial materials.
The latter is the first macrocyclic intermediate common to heme chlorophyll siroheme and b 12 itself. All vitamin b12 compounds contain the cobalt atom in its trivalent state. The vitamin is found in many animal products such as poultry beef eggs. Cyanocobalamin is the principal one used in vitamin supplements and pharmaceuticals.
Vitamin b 12 is an essential vitamin necessary for healthy nerve tissue brain function and red blood cell production. Vitamin b12 functions as a cofactor for methionine synthase and l methylmalonyl coa mutase. Vitamin b 12 occurs in several forms called cobalamins. Vitamin b 12 is not found in plants but ruminal and intestinal bacteria can synthesize adequate amounts if the diet contains sufficient cobalt approximately 0 1 0 2 mg cobalt per kg diet dry matter.
Vol 1 3 7th ed. Vitamin b12 is required for proper red blood cell formation neurological function and dna synthesis. There are at least three active forms. Vitamin b 12 is involved in the cellular metabolism of carbohydrates proteins and lipids.