Multiple Sclerosis Lymphoma Skin Lesions

Cutaneous t cell lymphomas mycosis fungoides affecting the breast or presenting initially as breast lesions are found in multiple case reports in the available literature.
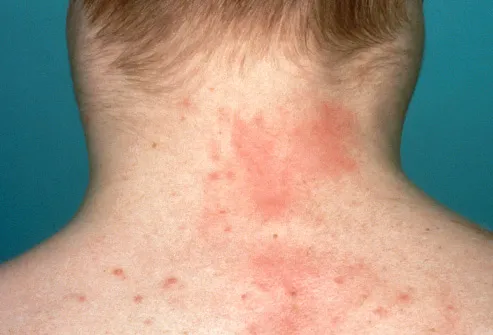
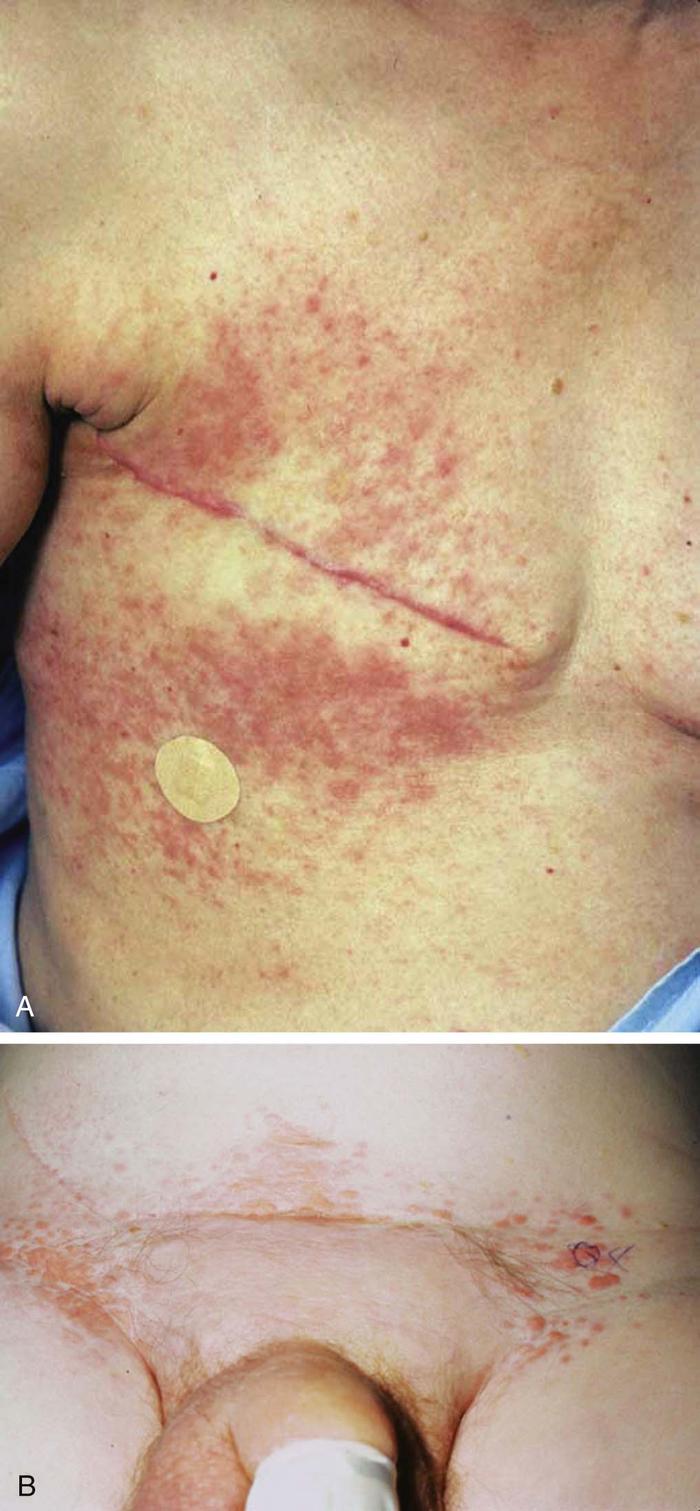
Multiple sclerosis lymphoma skin lesions. 1e and f based on the report cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma was suggested for. Mycosis fungoides mf is the other common form of cutaneous lymphoma characterized by red scaly patches or lesions on the skin. 298 300 cutaneous t cell lymphoma typically appears as brownish red patches with fine scale and delicate wrinkling on the skin of the trunk typically within. This is the most common b cell lymphoma of the skin.
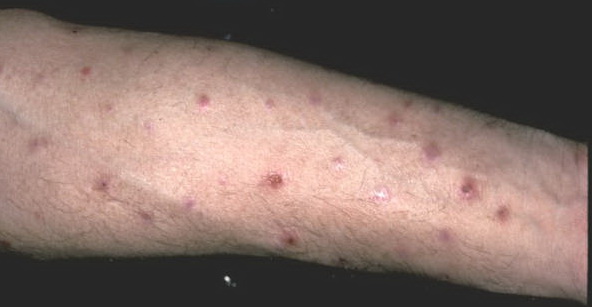
The characteristic features of primary cutaneous alcl include the appearance of solitary or multiple raised red skin lesions that do not go away have a tendency to ulcerate and may itch. It accounts for most of all cases of cutaneous t cell lymphomas. The patient was referred for a dermatology consultation and was scheduled for more detailed tests and a skin biopsy. Its diagnosis depends on patients history and clinical findings consisting of oral aphthae recurring at least 3 times a year plus any two findings out of genital ulcers or scars skin lesions such as erythema nodosum pseudofolliculitis or papulopustular lesions uveitis and positive pathergy test are required for the diagnosis.
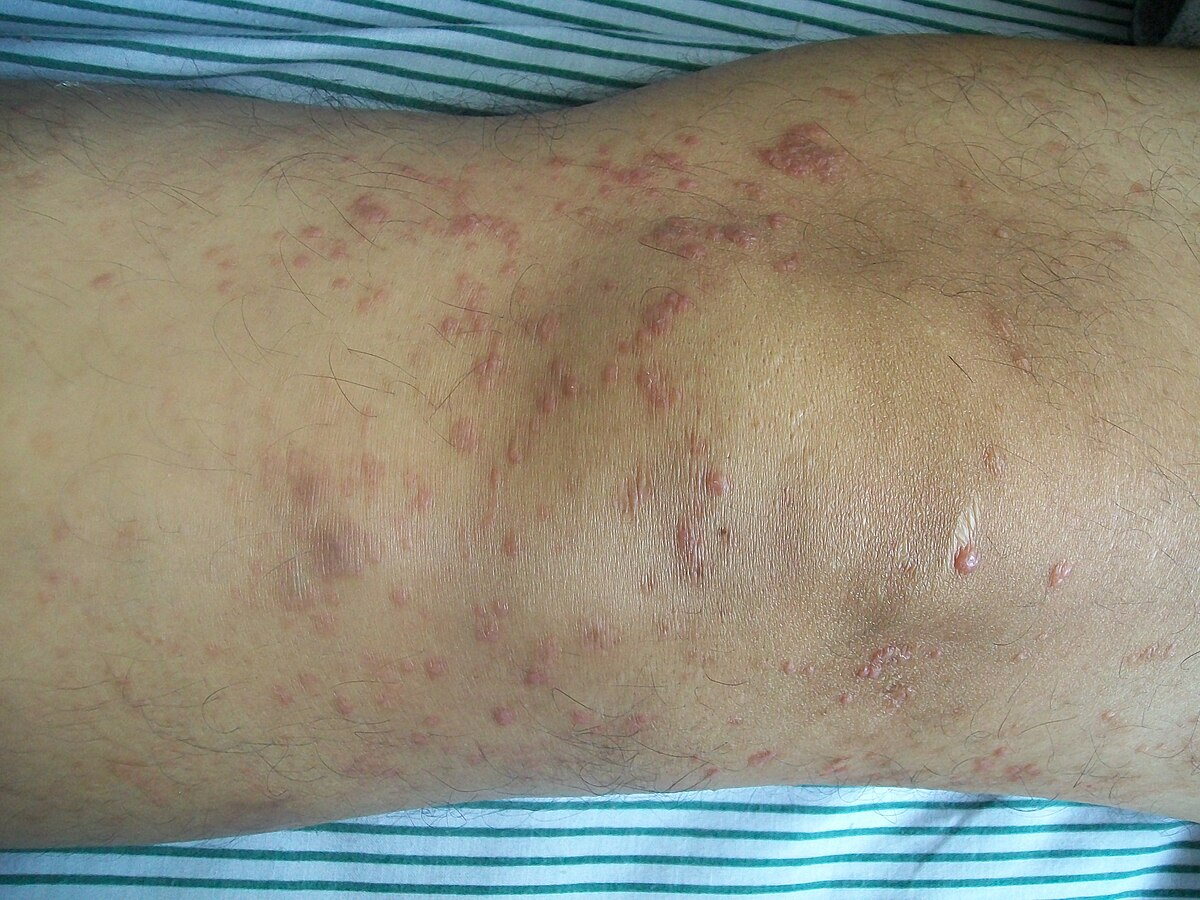
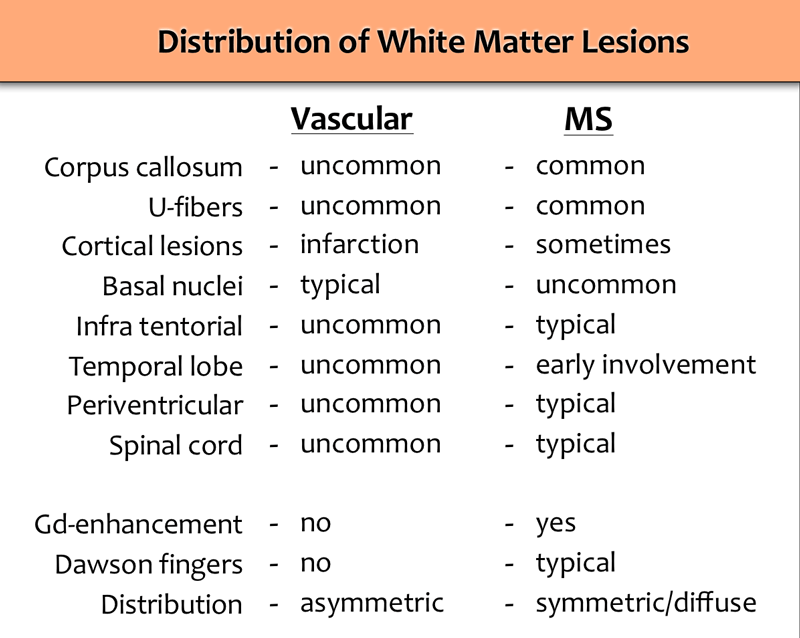
Multiple sclerosis multiple sclerosis is a demyelinating disease of unknown cause that more commonly affects young women. There may be only a single lesion but there can sometimes be a few. It appears as skin lesions that are red to purplish large pimples plaques raised or lowered flat lesions or nodules bumps on the arms or upper body. It tends to grow slowly.
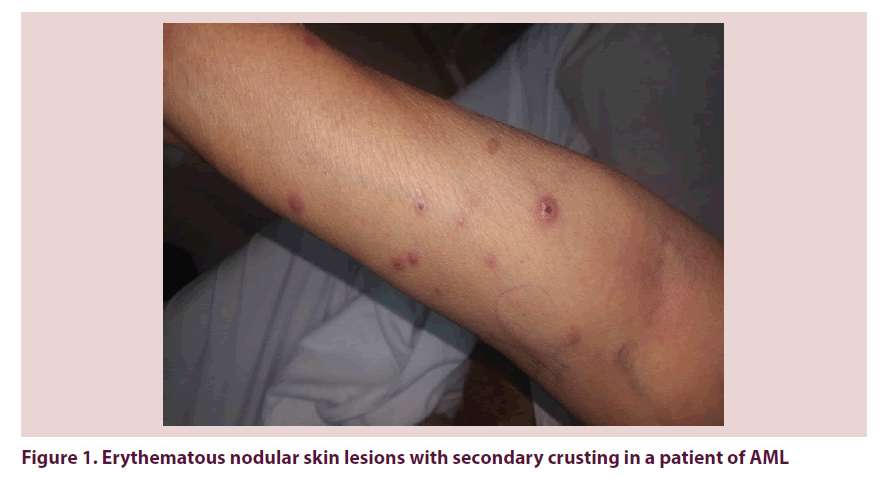
Objective reporting a case of cutaneous large cell lymphoma in a multiple sclerosis patient during fingolimod treatment. Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma. Only about 10 percent of the time does primary cutaneous alcl extend beyond the skin to lymph nodes or organs. Previous reports of cutaneous neoplastic lesions secondary to fingolimod treatment among multiple sclerosis patients.
An advanced form of mycosis fungoides is referred to as sezary syndrome.



/warning-signs-of-lymphoma-2252446-5bb7c5a8c9e77c0051315106.png)




/woman-scratching-her-legs-670895525-58920ddf5f9b5874eea222a1.jpg)